Main Takeaways:
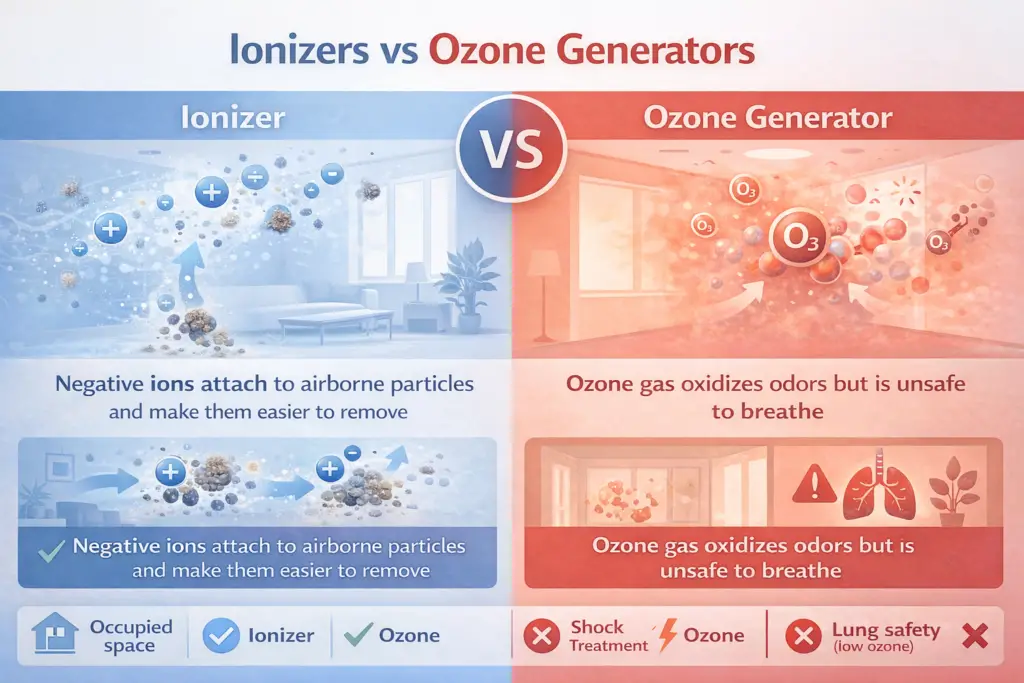
- Ionizers release negative ions that attach to airborne particles, making them easier to filter or causing them to drop out of the air.
- Ozone generators deliberately produce ozone gas, a powerful disinfectant that is unsafe to breathe directly.
- Ionizers may create small amounts of ozone as a byproduct, but they are not the same as ozone generators.
- Safe alternatives include smart purifiers with sensors and induct HVAC systems that neutralize contaminants before air reaches your living space.
Table of Contents
Ionizer vs. Ozone
What is an Air Ionizer?
An ionizer generates negatively charged ions and releases them into the air. These ions attach to particles like dust, pollen, and smoke, causing them to clump together and fall or get trapped by a filter.
Ionizers can also improve mood and may reduce symptoms of depression, according to studies.
*Example:* Imagine you run an ionizer in your living room during allergy season. The negative ions help pull pollen out of the air before it can make your eyes water. A HEPA filter could catch a lot of pollen too — but together, ionizer + filter give you the best shot at relief.
What is an Ozone Generator?
An ozone generator produces ozone (O₃), sometimes called “activated oxygen.” Ozone oxidizes contaminants, changing their chemical structure and disinfecting surfaces and air.
The problem is that ozone is highly reactive and damages lung tissue when inhaled.
That’s why ozone machines should never be used around people, pets, or plants. They are only safe in unoccupied spaces.
*Example:* A hotel might use an ozone generator to eliminate cigarette smoke odor between guests. The room is sealed, the machine runs for an hour or two, and only after the ozone dissipates is the room safe to occupy again.
Why Would Anyone Use Ozone?
At first glance, it seems crazy — why would you want something in your house that can damage your lungs?
But think about it: electricity can kill you if you touch a live wire, yet we power our homes with it every day.
Natural gas can explode, yet we rely on it for heat and cooking.
Ozone is the same kind of potent energy — dangerous if misused, but incredibly effective when controlled.
Are Ionizers Just Ozone Generators in Disguise?
No. Ionizers and ozone generators are often confused because both involve charged oxygen, but their purposes are very different:
- Ionizer: Designed to release negative ions for particle removal.
- Ozone Generator: Designed to flood a space with ozone gas for disinfection.
Most ionizers produce trace amounts of ozone as a byproduct. In a large, ventilated room this is usually safe, but in small enclosed spaces ozone can build up to irritating levels. Some ionizers even have an “away” or “ozone” mode that intentionally increases ozone output.
This is why it’s important to understand what your unit is designed to do.
Comparison Table: Ionizer vs. Ozone Generator
| Feature | Ionizer | Ozone Generator |
|---|---|---|
| Main Function | Releases negative ions to remove particles | Produces ozone gas to disinfect |
| Safety | Generally safe, but small ozone byproduct | Unsafe to breathe — only for unoccupied use |
| Best Use | Everyday air cleaning with filters | Shock treatment for odors/mold |
| Risks | Ozone buildup in small rooms | Lung irritation, plant/animal harm |
In other words: Ionizers clean the air gently over time, while ozone generators blast it with a disinfectant that’s too harsh to live in.
Ionizer Benefits and Risks
- Removes ultrafine particles smaller than what HEPA can capture.
- Works with filters by clumping fine particles together for easier capture.
- Potential mood-boosting effects from negative ions.
- Risk: trace ozone buildup in small or poorly ventilated spaces.
Ozone Benefits and Risks
- Extremely powerful disinfectant for odors, mold, and bacteria.
- Best used as a shock treatment in unoccupied spaces.
- Dangerous to lungs when inhaled, even at low concentrations over time.
Safer Alternatives
Smart air purifiers: Modern purifiers use HEPA + ionizer tech with air quality sensors that prevent unsafe ozone levels. Many can be controlled via smartphone for scheduling and alerts.
Induct air purifiers: Installed directly into HVAC ductwork, these units use plasma or PCO ionizers to treat air inside the system. See: Reme Halo
This effectively turns your HVAC into a whole-house purifier, with any trace ozone dissipating before air enters living spaces.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do ionizers produce ozone?
Yes, most ionizers create a small amount of ozone as a byproduct. A typical consumer ionizer produces less than 0.05 ppm, which is within limits considered safe by organizations like the FDA. However, in a tiny room with poor ventilation, ozone can build up. To be safe, always check that your device is labeled “ozone-free” or “CARB-certified.”
Is ozone ever safe to breathe?
No. Ozone is harmful to the lungs at any level above natural outdoor background levels. It can cause coughing, throat irritation, and worsen asthma. Ozone should only be used in unoccupied rooms for short-term disinfection — never as a continuous air cleaner.
Are ionizers better than HEPA filters?
Ionizers and HEPA filters do different jobs. HEPA filters physically capture 99.97% of particles down to 0.3 microns. Ionizers, on the other hand, clump ultrafine particles together so they fall out of the air or get caught by a filter more easily. The most effective units combine both technologies.
Can ionizers kill bacteria and viruses?
Some research suggests negative ions can disrupt bacterial cell membranes and deactivate viruses, but the effect is limited compared to medical-grade sterilization. Ionizers should be seen as a supplement to HEPA filtration, not a replacement for germicidal devices or proper hygiene.
What’s the safest alternative to an ozone generator?
Smart HEPA purifiers with ionizers, or HVAC induct systems, provide many of the same air-cleaning benefits without filling your space with ozone. They’re designed to monitor air quality, prevent unsafe levels of ions or gases, and run automatically when needed.
Summary
The difference: Ionizers release negative ions to clean particles from the air, while ozone generators deliberately produce ozone gas for disinfection.
The overlap: Ionizers may create small amounts of ozone, but not at the levels of dedicated ozone machines.
The rule: Never use ozone generators around people or pets, and only use ionizers in appropriate spaces.
For everyday clean air, a smart air purifier or an HVAC-based solution offers the benefits of ions without the risks of excess ozone.






